
More Indoor Sedentary Activities Results in More Weight Gain and Fat on Liver
Jun 2, 2020
Introduction
The Covid-19 pandemic has restricted your daily norms and activities. Increases maintain safe social distance, you are now spending more time on sedentary indoor activities – slacking in couch eating your favorite food, watching movies, playing games and shopping online. The consequences of lesser energy output? Increase body weight. In fact, Malaysia has the HIGHEST rate of obesity and overweight (64% male and 65% female) among Asian countries, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) [1]. This also shown to have an association with the high prevalence of fatty liver in the population [2]. Are you aware that your increasing body weight also simultaneously increases your risk of getting a fatty liver?
Those with central obesity (referring to your tummy!) are at high risk of having fats deposition in the liver, thus, forms fatty liver. The fattened liver in ducks or geese made a great delicacy around the world, but in humans, it causes health complications. Fatty liver in humans is a condition in which more than 5% of the liver is built up of fats. The Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is caused by several factors, and one of the common factors will be obesity or large waist size [4].
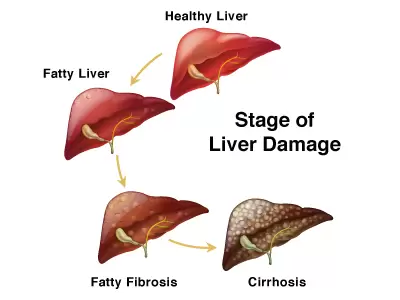
- Overweight and high-fat level in the blood circulation diminishes the metabolism of fats due to the insensitivity of hormone (insulin) in breaking down the fat molecules [5].
- The excess fats will then store in other cells such as liver [5]. The high amount of fat storage in the liver leads to fatty liver formation, and more prone to free radical attacks [5].
- Long term free radical attacks cause unpleasant inflammation and scar formation that forms liver fibrosis.
- Prolong liver fibrosis leads to impairment of liver cell formation, named cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is the last stage of liver damage, which has irreversible scarring.
Irreversible scarring is a big NO as it involves loss of liver cells and functions. Fret not! Both fatty liver and liver fibrosis are reversible. Take preventive steps before your liver condition gets worsen, you may start practicing a healthy diet or opt for a product that can help in repairing damaged liver cells.

- Essential Phospholipid ingredient: repair & regenerate healthy liver cells, especially the ingredient phosphatidylcholine (PC), that serves as the building blocks of the liver [6].
- Vitamin B group: aid in energy generation which needed during the healthy liver cells regeneration process [7]
- Vitamin E: to protect the liver from free radical attacks [8].
It is crucial in maintaining our liver health to ensure its optimum functions. Hence, starting from today, stop fattening your liver and be kind to your liver!
Livolin Forte
If you have fatty liver, you may try out Livolin Forte.
-
Find out more Livolin Forte
Livolin Forte is a health supplement providing Essential Phospholipids added with Vitamin B Complex and Vitamin E.
It is a Triple Action Formula that helps in liver regeneration and fasten its recovery, ensuring our liver healthy for its optimum functions.
References
- Malaysia and WHO call for more investment in primary health care the 21st century. 8 April 2019. World Health Organization. [cited 8 May 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/malaysia/news/detail/08-04-2019-malaysia-and-who-call-for-more-investment-in-primary-health-care-the-21st-century
- MALIK A, CHEAH P, HILMI I. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Malaysia: A demographic, anthropometric, metabolic and histological study. Journal of Digestive Diseases. 2007;8(1):58-64.
- Causes of Obesity [Internet]. Maso.org.my. 2019 [cited 2 August 2019]. Available from: http://www.maso.org.my/spom/chap5.pdf
- Symptoms & Causes of NAFLD & NASH | NIDDK [Internet]. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2019 [cited 2 August 2019]. Available from: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/nafld-nash/symptoms-causes
- Polyzos S, Kountouras J, Mantzoros C. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism. 2019;92:82-97.
- Gundermann K, Kuenker A, Kuntz E. Activity of essential phospholipids (EPL) from soybean in liver diseases. Pharmacological Reports. 2011;63(3):643-659.
- Laquale K. B-Complex Vitamins’ Role in Energy Release. Athletic Therapy Today. 2006;11(6):70-73.
- Sato K, Gosho M, Yamamoto T, Kobayashi Y. Vitamin E has a beneficial effect on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrition. 2015 Jul 1;31(7-8):923-30.



