
Benefits of Astaxanthin
Jul 22, 2019
Introduction
Skin is the largest organ as it is one-sixth of the total body weight. It acts as a chemical and physical barrier to protect the body against harmful external environmental agents [1]. However, if our skin leaves unprotected and exposes to excessive sunlight, it will result in sunburn and can also lead to photo-induced oxidation, inflammation, immunosuppression, aging and even carcinogenesis of skin cells [2]. Astaxanthin can revitalize these photoaging damages in quenching those oxidative stress and inflammation in all skin layers [3,4].
Astaxanthin – Protects Against Aging in All Skin Layers
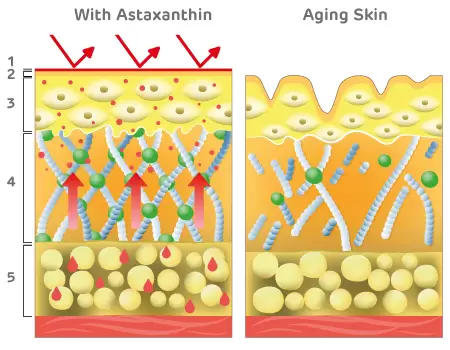
1. Surface: Astaxanthin serves as skin protective barrier against free radical damage [5]
2. Stratum Corneum: Astaxanthin fights skin dryness and skin roughness [6]
3. Epidermis: Astaxanthin quenches over-production of melanin [6]
4. Dermis: Astaxanthin fight lines and wrinkles and boosts fibroblast and collagen integrity [6,7]
5. Hypodermis: Astaxanthin improves nutrient supplies to the skin tissue [8,9]
Multifunctional Health Benefits of Astaxanthin
Besides skin health, Astaxanthin also exhibits health benefits on different part of our body.
1. Vision & Eye Health: Astaxanthin can improve capillary blood flow which relieves Computer Vision Syndrome such as eye fatigue, eye irritation and blurred vision [10,11]
2. Muscle Endurance: Astaxanthin can boost muscle endurance and recovery, lower lactic acid and muscle fatigue, reduce muscle damage and inflammation [12,13]
3. Cardiovascular Health: Astaxanthin can improve blood lipid profile, reduce oxidative stress and enhance capillary circulation [14,15]
4. Immune Health: Astaxanthin can enhance immune response, strengthen and balance the immunity [16]
5. Digestive Health: Astaxanthin can lower gastric inflammation and decrease H. pylori infection [17,18]
6. Brain Health: Astaxanthin can improve age-related forgetfulness and alertness [19]
BiO-LiFE Astaxanthin Range
Find out more :
BiO-LiFE Astaxanthin 4mg : http://Biolife.2.vu/Astaxanthin4mg_1
BiO-LiFE Astaxanthin 6mg : http://Biolife.2.vu/Astaxanthin6mg_1
References
- Pérez-Sánchez A, et al. Nutrients 2018; 10(4): 403.
- Guerin M, et al. TRENDS in Biotechnology 2003;21(5): 210-6.
- Kim JH, et al. Journal of Medicinal Food 2011; 14(11):1469-75.
- Uchiyama A, J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2008; 43(1): 38-43.
- Ambati R, et al. Marine drugs 2014; 12(1): 128-152.
- Tominaga K, et al. Acta Biochimica Polonica 2012; 59(1): 43-47.
- Tominaga K, et al. Journal of clinical biochemistry and nutrition 2017; 61(1): 17-35.
- Saito M, et al. Graefe’s archive for clinical and experimental ophthalmology 2012; 250(2): 239-245.
- Miyawaki H, et al. Journal of clinical biochemistry and nutrition 2008; 43(2): 69-74.
- Nagaki Y, et al. J Trad Med 2002; 19: 170-173.
- Shiratori K, et al. Journal of Clinical Therapeutics and Medicines 2005; 21(6): 637-650.
- Malmsten C, et al. Carotenoid Science 2008; 13: 20-22.
- Sawaki K, et al. Journal of Clinical Therapeutics & Medicines 2002; 18(9): 1085-1100.
- Satoh A, et al. Journal of clinical biochemistry and nutrition 2009; 44(3): 280-284.
- Yoshida H, et al. Atherosclerosis 2010; 209(2): 520-523.
- Lin KH, et al. International journal of molecular sciences 2016; 17(1): 44.
- Bennedsen M, et al. Immunology Letters 2000; 70(3): 185-189.
- Kupcinskas L, et al. Phytomedicine 2008; 15(6-7): 391-399.
- Grimmig B, et al. Geroscience 2017; 39(1): 19-32.



